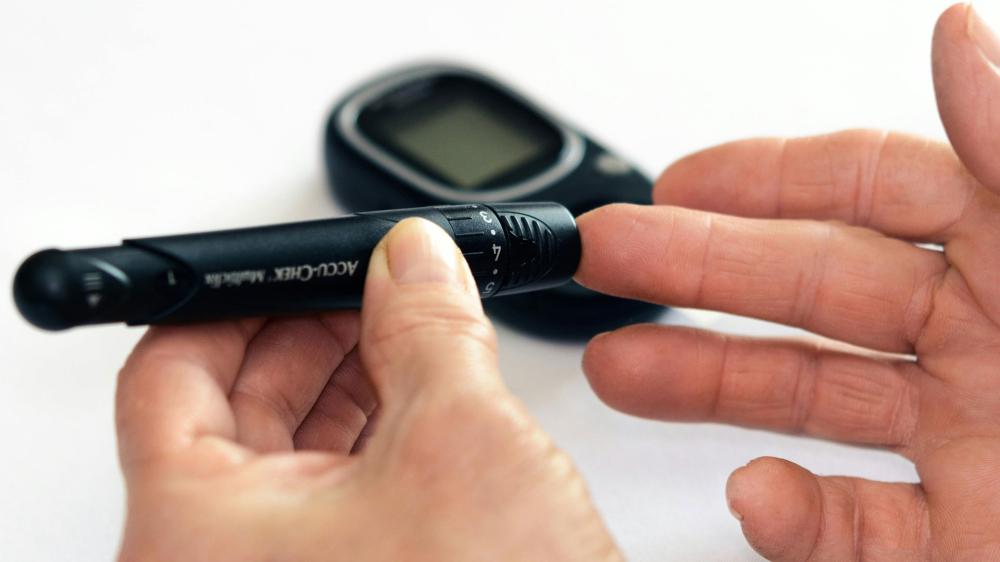
🧬 What Is Type 1 Diabetes?
- An autoimmune condition where the body attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
- The body produces little or no insulin, so glucose can’t enter cells for energy.
- Previously called juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes.
👶 Are You Born With It?
- No, it can develop at any age (not just in childhood).
- Around 50% of new cases are adults.
🔍 Type 1 vs. Other Diabetes Types
- Type 1: No insulin production.
- Type 2: Insulin is made, but the body becomes insulin resistant.
- Secondary diabetes: Loss of insulin-producing cells due to injury or illness, not the immune system.
⚠️ Symptoms
- Rapid onset:
- Extreme thirst & frequent urination
- Weight loss despite eating
- Fatigue, vision changes, mood shifts
- Fruity-smelling breath, vomiting
- In kids:
- Bed-wetting, frequent diaper changes, belly pain, fast breathing
- In adults (LADA): Slow onset, often misdiagnosed as Type 2.
🧬 Causes & Genetics
- Exact cause unknown, but likely a mix of genes and triggers (infections, viruses).
- Family history increases risk:
- If father has it → 1 in 17 chance
- If mother has it → 1 in 25 (before age 25), or 1 in 100 (after age 25)
- If both parents have it → up to 1 in 4 chance
🧪 Diagnosis
- A1c test: Measures 3-month blood sugar average (≥6.5% indicates diabetes)
- Fasting glucose: ≥126 mg/dL
- Random glucose: ≥200 mg/dL
- To determine Type 1 specifically:
- Autoantibody test
- Ketone test (in urine)
🌍 Health Disparities
- Type 1 diabetes rates are rising in the U.S., with Hispanic and Black communities facing worse outcomes.
- Structural racism in healthcare and other systems contributes to this.
💉 Treatment
- Daily insulin is required. Types:
- Rapid-acting (15 mins)
- Short-acting (30 mins)
- Intermediate (2–4 hrs)
- Long-acting (lasts ~24 hrs)
- Methods:
- Injections (vials/syringes or pens)
- Inhaled insulin (not for smokers or people with lung disease)
- Insulin pumps (worn on body)
📊 Glucose Monitoring
- Finger-prick tests or
- Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) with real-time alerts
💊 Other Medications
- Aspirin (heart protection)
- Cholesterol meds
- Blood pressure meds
🌿 Living With Type 1 Diabetes
- Sleep: Aim for 7+ hours
- Stress management: Support or therapy
- Quit smoking: Including vaping and chewing tobacco
📚 Reference:
This article was created based on trusted medical information from WebMD. You can view the full source here: